Views: 96 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-09-13 Origin: Site








Applications of Blue Laser in Dentistry
Blue laser (typically referring to lasers in the 400–500 nm wavelength range, such as the 445 nm diode laser) has gained attention in dentistry due to its unique properties, including high precision, selective absorption, and antibacterial effects. Below are the key applications and advantages of blue laser in dental practice.

1. Caries Detection and Diagnosis
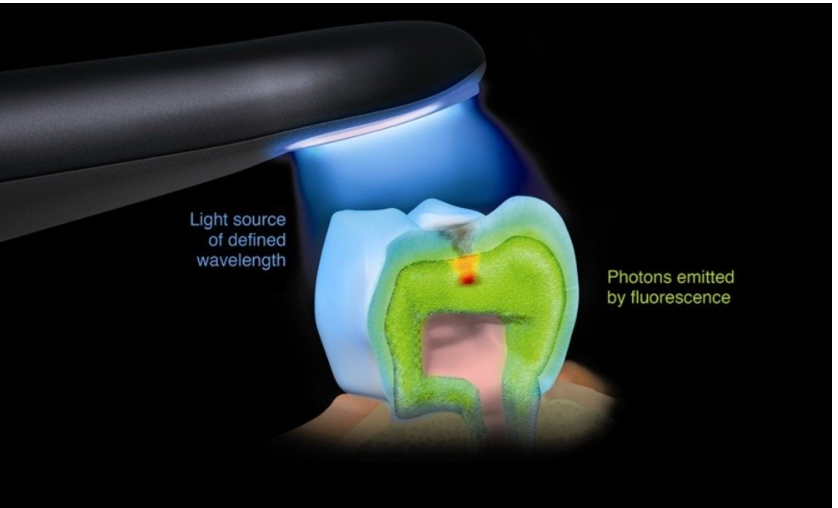
Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF):
Blue laser excites fluorescent compounds (e.g., porphyrins produced by bacteria) in carious tissue, allowing differentiation between healthy enamel and decayed areas (e.g., Diagnodent devices).
Advantages: More sensitive than X-rays for early caries detection, radiation-free, suitable for children and pregnant women.
2. Caries Treatment and Cavity Preparation
Selective Ablation of Carious Tissue:
The 445 nm blue laser is absorbed by pigmented decayed tissue, enabling precise removal while preserving healthy tooth structure.
Advantages: Minimally invasive, reduces patient anxiety (no drill noise), and conserves more natural tooth material.
3. Teeth Whitening
Activation of Bleaching Agents:
Blue laser accelerates the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (whitening agent), enhancing oxidation and reducing treatment time.
Controversy: Some studies suggest potential pulp temperature rise, requiring careful energy control.
4. Light-Curing of Composite Resins
Alternative to Conventional Curing Lights:
Blue laser (e.g., 450 nm) provides deeper and more uniform polymerization of composite resins, reducing shrinkage and improving marginal seal.
Advantages: Better curing depth, less post-operative sensitivity.

5. Periodontal Therapy and Antibacterial Effects
Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy (aPDT):
Blue laser combined with photosensitizers (e.g., methylene blue) kills anaerobic bacteria (e.g., P. gingivalis) in periodontal pockets.
Advantages: Reduces antibiotic use and minimizes bacterial resistance.
6. Soft Tissue Surgery
Gingivectomy and Frenectomy:
The 445 nm blue laser allows precise soft tissue cutting with excellent hemostasis and faster healing.
Advantages: Minimal bleeding, reduced swelling, ideal for pediatric patients or those with bleeding disorders.
7. Biostimulation Effects
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
Blue laser at low intensities promotes tissue healing in oral ulcers and periapical inflammation while reducing pain and swelling.


Key Considerations
Safety: Blue laser can harm the retina—protective eyewear is mandatory.
Parameter Control: Excessive energy may increase pulp temperature (cooling is essential).
Cost: Higher initial investment, more suitable for specialized clinics.
Future Directions
AI Integration: Automated caries detection using AI-assisted laser diagnostics.
Nanomaterial Enhancement: Gold nanoparticles to boost antibacterial effects.
Blue laser technology represents a shift toward minimally invasive and precise dentistry. However, its use should be carefully evaluated against other dental lasers (e.g., Er:YAG or CO₂ lasers) based on clinical needs.